



Global soil degradation is advancing at ~1 million km² per year, roughly the size of Egypt,
now impacting ~15 million km², degrading fertility, impeding carbon sequestration, and
threatening food security.
Depleted organic matter and nutrient loss, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions,
have led to yield declines, erosion, and rising costs for inputs like fertilizer.
Urgent interventions are needed to reverse degradation, rebuild fertility, and stabilize.


Biochar is a stable, porous, carbon-rich material produced via pyrolysis of biomass waste. It enhances soil aeration, water retention, nutrient holding capacity (CEC), and pH buffering. It also represents circular waste management, turning agricultural residues into valuable soil amendments, and contributes to carbon sequestration.
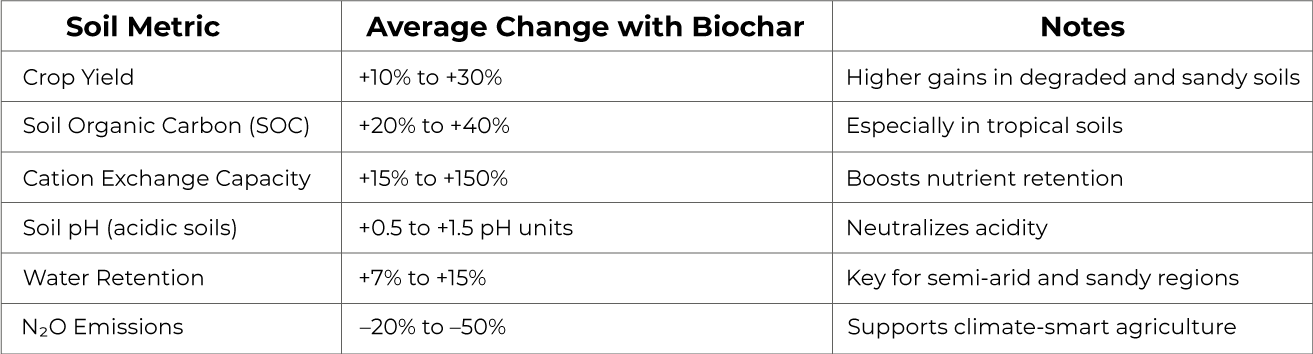
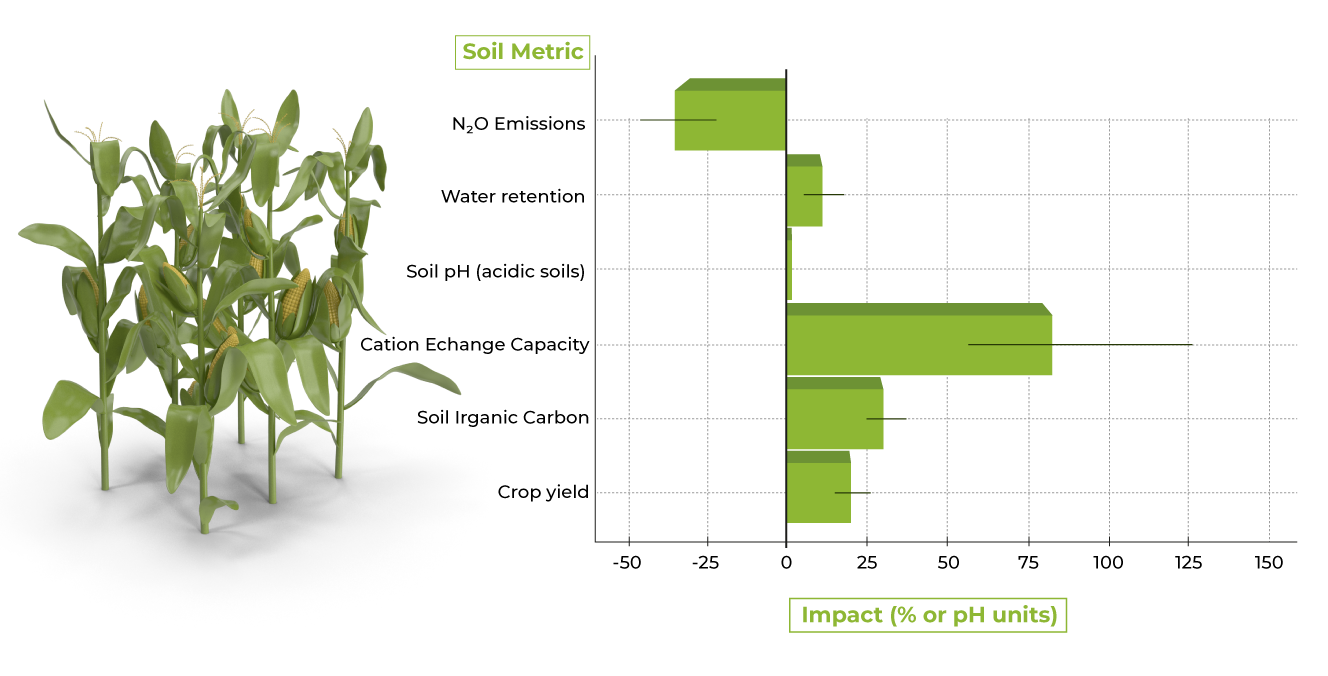
Biochars effectiveness varies by soil type, feedstock, and climate, but the results are consistently positive. Below is a synthesis of meta-analysis findings from 50+ studies covering different regions and crops:

FAO. (2023). The Status of the World’s Soil Resources. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
https://www.fao.org/global-soil-partnership/resources/highlights/detail/en/c/1270942/
Glaser, B., Lehmann, J., & Zech, W. (2002). Ameliorating physical and chemical properties of highly weathered soils in the tropics with charcoal – a review. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 35, 219–230.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-002-0466-4
Jeffery, S., Verheijen, F. G. A., van der Velde, M., & Bastos, A. C. (2011). A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 144(1), 175–187.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.08.015
Laird, D. A., Brown, R. C., Amonette, J. E., & Lehmann, J. (2009). Review of the pyrolysis platform for coproducing bio-oil and biochar. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 3(5), 547–562.
https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.169
Lehmann, J., & Joseph, S. (2015). Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Schmidt, H. P., Hagemann, N., Draper, K., & Kammann, C. (2019). The use of biochar in animal farming. IBI Biochar White Paper.
https://www.biochar-international.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Biochar-Animal-Farming.pdf
Woolf, D., Amonette, J. E., Street-Perrott, F. A., Lehmann, J., & Joseph, S. (2010). Sustainable biochar to mitigate global climate change. Nature Communications, 1, Article 56.
https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1053
Yeboah, S., Zhang, R., Cai, L., et al. (2019). Biochar addition in soil modifies the dynamics of soil nutrients and improves yield and quality of tomato: A meta-analysis. Scientia Horticulturae, 246, 61–73.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.10.058